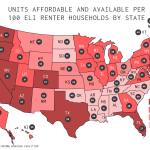
The landscape of employment is undergoing a transformation as AI and labor market changes converge, raising crucial questions about the future of work. Recent studies highlight the profound artificial intelligence impact on various industries, illustrating how technology labor disruption is not merely a theoretical concern but a tangible reality shaping job market trends today. As researchers delve into over a century of occupational churn, they unveil significant shifts in labor dynamics, prompting both anxiety and optimism among workers. The data signals a departure from traditional roles as automation and AI begin to redefine job functions and workforce demands. Understanding these trends will be essential for workers and businesses alike as they navigate the complexities of an evolving employment environment.
The evolution of the workforce, intertwined with technological advancements, is leading to remarkable shifts in employment patterns. As we analyze the implications of machine learning and automation on various sectors, it becomes clear that the very essence of work is being redefined. This transformation prompts us to consider how emerging technologies influence occupational stability and the new skills required in a competitive job market. With workforce dynamics increasingly characterized by the integration of smart systems, the dialogue around the effects of these innovations on employment continues to expand. Emphasizing the need for adaptability and ongoing education is vital for both companies and employees as they prepare for the realities of tomorrow’s labor landscape.
The Evolution of the U.S. Labor Market and Technology
Over the past century, the U.S. labor market has undergone significant transformations, largely influenced by technological advancements. The introduction of new technologies has led to shifts in occupational demand, creating what economists describe as ‘occupational churn.’ Historical data indicates that while there was a period of relative stability in the job market between 1990 and 2017, new evidence suggests that the introduction of artificial intelligence (AI) is catalyzing a new wave of change. Researchers David Deming and Lawrence H. Summers have drawn from over 124 years of U.S. Census data to illustrate how each technological wave affects job distribution and market dynamics.
These shifts reflect broader job market trends, revealing not just the rise of new professions, but a transformation in skills required by employers. Many traditional roles are diminishing due to automation, whereas sectors like science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) are experiencing exponential growth. This transition speaks to the broader implications of AI and its defining role in the future of work, challenging workers to adapt to an increasingly tech-centric job landscape.
AI and Labor Market Changes: Emerging Trends
The introduction of AI into the labor market has brought about notable emerging trends that warrant examination. Recent studies highlight a significant upward trend in high-skilled employment roles while simultaneously marking a decline in low-wage job opportunities. Deming’s research suggests that while fears of job polarization—whereby low-paid, low-skill jobs grow at the expense of middle-tier positions—dominated economic discussions in the early 2000s, the late 2010s saw a reversal, with high-paid jobs soaring. This shift illustrates that AI contributes not only to job creation in high-skill sectors but also to a noticeable gap in wage distribution.
Moreover, the rapid growth of STEM jobs indicates a labor market increasingly oriented towards technical expertise. As organizations make substantial investments in AI and frontier technologies, they prioritize hiring highly skilled talent. The workforce must respond to these demands by focusing on technological proficiency, as evidenced by the dramatic increase in software developers and data analysts within the job market. This evolution underscores the extent to which technology labor disruption is reshaping occupational landscapes, necessitating proactive workforce planning to harness the capabilities that AI empowers.
Changing Dynamics in Low-Paid Service Work
The ramifications of AI go beyond high-skilled employment; they extend deeply into sectors traditionally reliant on lower-wage service work. According to the research findings, there has been a stark decline in low-paid positions, particularly in retail and service industries, where job options have diminished significantly since 2019. This decline raises questions about the future viability of these roles, considering the ongoing advancements in AI and automation. For instance, the retail sector witnessed a notable drop in employment share, highlighting the critical need for service industries to adapt or risk obsolescence.
Moreover, while historical patterns showed a growth in low-wage service jobs from 1980 to the early 2000s, the current trend suggests a plateau or potential decline, reinforcing the impact of AI on employment dynamics. This shift reflects broader economic realities, including increased wage demands and labor market tightness, compounded by disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. As businesses navigate these changes, they must balance the imperatives of leveraging technology while ensuring that service roles adapt to a new reality defined by AI and automation.
The Future of Work: Insights from Automation
As we navigate the complexities of the modern labor market, the impact of automation becomes increasingly clear. Automation, while historically feared for its potential to displace workers, also presents opportunities for efficiency and enhanced productivity in knowledge-centric sectors like finance and management. Deming outlines that while automation has the power to eliminate certain job functions, it may also lead to heightened expectations from employers regarding output and quality of work. This paradox presents a dual challenge for modern employees who must leverage new technologies to meet evolving workplace demands.
Furthermore, the insights shared by economists emphasize that the future of work will likely be defined by a delicate balance between leveraging AI tools and maintaining the human element essential for many professions. As organizations seek to maximize AI’s advantages, employees will need to cultivate skills that complement this technology, ensuring they remain relevant in an increasingly automated economy. Thus, understanding the interplay between automation and employment will be critical for stakeholders aiming to create sustainable job opportunities amidst the ongoing technological transformation.
Occupational Churn: The Paradox of Job Security
Amidst fears of automation and job displacement, the concept of occupational churn provides a nuanced perspective on job security in the face of technological upheaval. Historical analysis reveals that while certain sectors have experienced volatility, others have remained resilient, adapting to changes wrought by innovation. The research on occupational churn indicates that the labor market has historically shown patterns of both growth and decline, dependent on the types of technologies that emerge. In many cases, despite the disruption caused by new technologies, the overall employment landscape has restructured rather than collapsed.
Additionally, awareness of this cyclical nature of the labor market can empower workers to navigate transitions more effectively. As AI continues to reshape the employment landscape, understanding the mechanisms of churn can aid in strategizing career paths, enhancing skills in anticipation of emerging demands. By fostering adaptability, workers may better protect themselves against potential job loss caused by automation, ultimately contributing to a more resilient and dynamic workforce.
Automation Anxiety: Reassessing Worker Perspectives
The phenomenon known as ‘automation anxiety’ encapsulates the uneasiness workers feel regarding job security in an increasingly automated environment. This concern is not unwarranted, as reports have suggested that a significant percentage of jobs are at risk of being automated. Yet, as Deming and his colleagues point out, while automation has indeed resulted in job displacement, the broader narrative is more complex. Many sectors have also seen the creation of new job opportunities resulting from technological advancements, challenging the prevailing notion of total job loss.
As the workforce grapples with the implications of AI, there is a critical need to shift the focus from anxiety to opportunity. By embracing the capabilities of AI and recognizing the potential for increased productivity, workers can transform their perspectives on automation. This entails not only upskilling and reskilling in response to AI-driven changes but also fostering an organizational culture that champions innovation and continuous learning, ensuring that they remain integral to the evolving job market.
Investment in AI: Changing the Job Market Landscape
Investment in AI technologies has gained unprecedented momentum, dramatically altering the job market landscape. According to recent findings, companies are now allocating substantial resources towards AI systems, resulting in notable shifts in employment patterns across various industries. The pursuit of tech talent, particularly in STEM fields, reflects a paradigm shift where businesses prioritize skills that align with emerging AI capabilities. This emphasis on cutting-edge technology not only enhances organizational efficiency but also defines the skill sets required for future workers.
The growing significance of AI investment elucidates the changing nature of work, as organizations leverage these technologies to remain competitive. Furthermore, as AI continues to reshape job functions, the demand for qualified technicians, data analysts, and software developers is projected to surge. Therefore, understanding the landscape of AI investment is crucial for workers aiming to position themselves advantageously in a rapidly evolving job market.
Trends in High-Paying Job Growth
Recent analyses reveal a substantial uptick in high-paying job opportunities, signaling a transformative shift in the labor market as AI gains traction. These positions, often requiring specialized skills and advanced education, are increasingly seen as critical to organizational success. As industry leaders prioritize recruiting top talent in fields such as computer science, engineering, and data analysis, the wage disparity between high and low-skilled jobs continues to widen. This trend highlights the importance of education and continuous skill development as workers adapt to a changing economic landscape.
Moreover, the growth of high-paying roles goes hand-in-hand with the decline of traditional employment pathways. The labor market is increasingly polarized, with high-skill positions flourishing while many middle-skill jobs continue to diminish. This shift calls for a reevaluation of workforce training programs and educational curriculums to better prepare future workers for the demands of an AI-driven economy, underscoring the vital role of innovation and adaptability in career success.
The Accelerating Impact of E-Commerce on Retail Jobs
The rise of e-commerce has profoundly impacted retail employment, leading to a significant decline in traditional retail jobs. The synergy between AI and e-commerce platforms has accelerated this trend, as companies leverage predictive technologies to enhance customer experiences and streamline operations. The data suggests a marked reduction in retail sales jobs, dramatically reshaping the employment landscape for workers in this sector. This trend is likely compounded by changing consumer habits, where households increasingly favor online shopping over in-store experiences.
As the retail sector adjusts to these changes, organizations must confront the implications of diminished job opportunities for workers. Transitioning to a workforce model that embraces technology will be crucial for retail companies, as they seek to navigate the complexities posed by the simultaneity of AI adoption and shifts in consumer behavior. The future of retail hinges on innovation alongside human-centered strategies, ensuring that remaining retail roles evolve in line with technological advancements.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is artificial intelligence impacting the labor market today?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is significantly shaking up the labor market by driving changes in job distribution and creating new opportunities in high-skilled sectors. Recent research highlights an increase in high-paying jobs, particularly in STEM fields, as well as a decline in traditional low-paying service roles, suggesting AI’s powerful influence on workforce dynamics.
What are the key trends associated with job market changes due to AI?
The key trends linked to job market changes driven by AI include the end of job polarization, increased demand for STEM-related jobs, a drastic decline in low-paid service positions, and significant reductions in retail sales jobs. These trends indicate that the labor market is evolving towards higher compensation roles, which AI is helping to facilitate.
What does occupational churn mean in relation to AI and labor market changes?
Occupational churn refers to the fluctuation of employment shares among different professions over time. In the context of AI and labor market changes, it illustrates how technological disruptions lead to shifts in job availability and the skill sets required, indicating a transition towards professions that are increasingly reliant on advanced training in technology.
Is AI causing job displacement across all sectors?
While AI is indeed driving job displacement, particularly in low-wage sectors such as retail and services, it is also creating new job opportunities in STEM fields. The net effect of AI on the job market is complex, with some roles becoming obsolete while others emerge that require advanced skills and training.
How can workers adapt to the labor market changes induced by AI?
Workers can adapt to the labor market changes brought about by AI by upskilling and reskilling in areas that are in high demand, particularly in technology and STEM-related roles. Continuous learning and embracing new technologies will be crucial for career resilience in an increasingly AI-driven job market.
What role does technology labor disruption play in the future of work?
Technology labor disruption, particularly through AI, plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of work by transforming job structures, enhancing productivity, and altering skill requirements. As companies increasingly invest in AI technologies, the workforce will need to evolve to meet new demands, ensuring that workers possess the necessary skills to thrive.
Will AI create more job opportunities than it displaces in the labor market?
There is an ongoing debate about whether AI will create more job opportunities than it displaces. Current research suggests that while some low-skilled jobs may decline, the growing demand for high-skilled positions, particularly in tech, indicates that AI could ultimately lead to a net increase in job opportunities if the workforce adapts accordingly.
How has historical data on technology disruption informed our understanding of AI’s impact on jobs?
Historical data on technology disruption, particularly the analysis of occupational churn over the past century, has revealed patterns of stability and volatility in the labor market. This analysis helps clarify how past technological advancements have transitioned from displacement to job creation, providing insights into the potential future impacts of AI on employment.
What should companies consider when integrating AI into their workforce?
When integrating AI into their workforce, companies should consider the potential for job displacement and the need for employee training. Organizations must balance technological adoption with strategies for upskilling staff, fostering an environment where employees can thrive alongside AI advancements.
What is the significance of STEM job growth in the context of AI and labor market trends?
The growth of STEM jobs is significant in the context of AI and labor market trends, as it reflects an increasing demand for high-skilled roles that are essential to advancing technology. As AI continues to reshape industries, the expansion of STEM positions highlights the necessity of technical expertise and illustrates the shift towards an economy driven by innovation.
| Key Trends of AI Impact on Labor Market | |
|---|---|
| Trend 1: Job Polarization | Emergence of high-paying jobs and decline of middle-income positions |
| Trend 2: Growth of STEM Jobs | Increase in STEM job share from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% in 2024, almost 50% increase |
| Trend 3: Decline of Low-Paid Service Jobs | Flat or declining employment in low-paid service sectors since 2019 |
| Trend 4: Reduction in Retail Sales Jobs | 25% drop in retail sales jobs from 2013 to 2023, rapid growth of e-commerce |
Summary
AI and labor market changes are fundamentally reshaping the workforce, with evidence highlighting a shift towards high-paying jobs and a notable decline in low-paid service roles. As technology continuously disrupts traditional employment patterns, workers must adapt to these transitions, analyzing the evolving job landscape. This research illustrates how AI not only influences employment distribution but also accelerates shifts that were already in motion, indicating a future workforce that demands higher skills and adaptability.