The housing crisis in the USA has reached alarming levels, leaving many Americans grappling with the harsh realities of housing affordability. Rising home prices have outpaced wage growth, making it increasingly difficult for aspiring homeowners to enter the market. Contributing factors include stringent land-use regulations, often referred to as “NIMBY” (Not In My Backyard), which hinder construction productivity and innovation. As these policies persist, they stifle large-scale projects that could otherwise alleviate the housing shortage. A thorough analysis of the housing market reveals a pressing need for reform to address these challenges and promote sustainable real estate trends.
The ongoing predicament surrounding housing availability in the United States reflects a growing concern for many. This dilemma often manifests as a significant strain on citizens’ ability to find affordable living options within their communities. Factors such as overly restrictive land use regulations and a reluctance to support new development play a key role in this crisis, which has sparked widespread discussions about the future of urban residence. As we delve into this topic, it becomes crucial to explore the connections between construction practices and real estate market dynamics, especially in light of current economic conditions.
Understanding the Housing Crisis in the USA
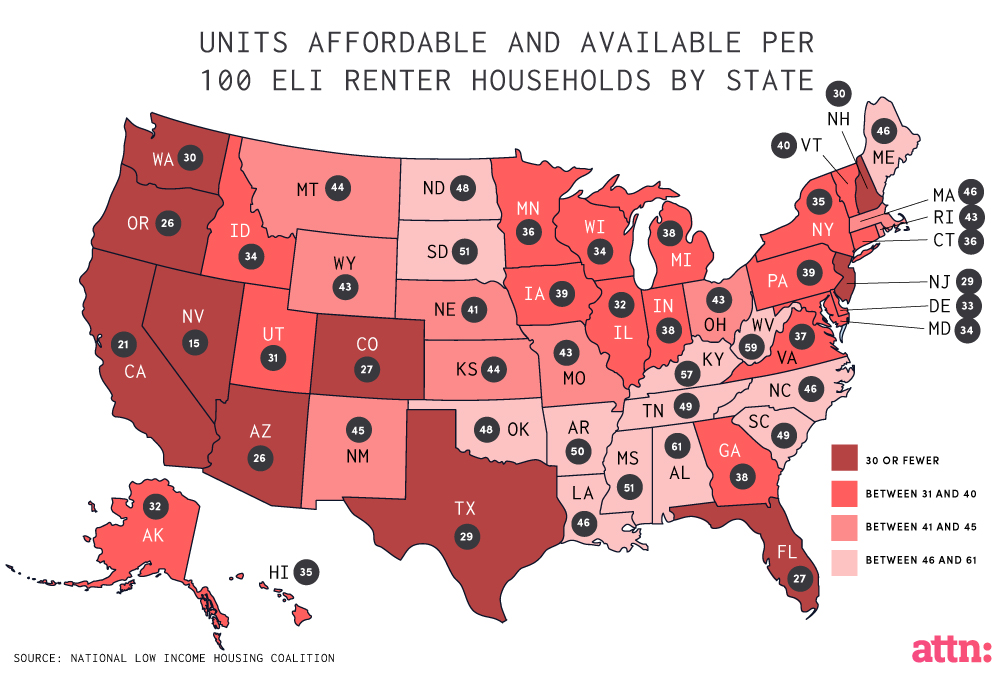
The housing crisis in the USA has emerged as a significant challenge in recent years, impacting countless families and individuals seeking affordable living options. Factors such as rising home prices, stagnating wages, and the limited availability of new construction all contribute to a landscape where housing affordability is rapidly diminishing. The disconnect between income levels and housing prices has intensified, leaving many Americans trapped in a cycle of instability, with ownership becoming increasingly elusive.
One of the key aspects driving the housing crisis in the USA is the restrictive land-use regulations often influenced by NIMBY (Not In My Back Yard) sentiments. These policies have made it cumbersome for builders to develop new projects, leading to a decrease in large-scale housing production. Consequently, less innovation within the construction sector, coupled with rising demand for homes, has exacerbated the affordability issue and contributed to a stagnant housing market.
NIMBY Land Use Policies: Impact on Housing Affordability
NIMBY land use policies play a pivotal role in the current housing affordability crisis. Under the guise of protecting neighborhood standards, these regulations often result in heightened restrictions that stifle new development and innovation within the construction industry. By preventing the establishment of larger housing projects that could benefit from economies of scale, communities effectively limit the supply of available homes, pushing prices ever higher.
Moreover, the policies create an environment where smaller builders and developers dominate the housing market, resulting in fewer options for potential homeowners. These small-scale constructions rarely achieve the same level of efficiency as larger developments, which were historically responsible for producing affordable housing units. Thus, the emphasis on individual neighborhood concerns compromises the broader societal need for accessible and affordable housing.
Construction Productivity: A Key to Solving the Housing Market Crisis
The decline in construction productivity has emerged as a critical factor in the U.S. housing market analysis. Research indicates that since the 1970s, the construction sector has consistently lagged behind other industries in terms of output per worker. With fewer innovations and reliance on smaller scale projects, builders face increased costs and delays that inevitably lead to higher housing prices.
Improving construction productivity could unlock solutions to the housing affordability crisis by allowing for more efficient homebuilding practices. Enhanced construction methods and technologies could pave the way for builders to maximize economies of scale while reducing overall costs. This uptick in productivity, combined with thoughtful land-use strategies, could help mitigate the affordability crisis and make homeownership attainable for more Americans.
Analyzing Real Estate Trends: The Future of Housing
As the housing crisis continues to unfold, analyzing real estate trends becomes crucial for understanding potential solutions. Trends indicate a shift towards more sustainable practices and innovative construction techniques that might alleviate some pressure on housing prices. With an increasing number of consumers prioritizing eco-friendly homes, builders are incentivized to adopt more productive practices that enhance their efficiency while meeting contemporary demands.
Furthermore, the current economic climate necessitates a reevaluation of zoning laws and land development policies to encourage affordable housing. By striking a balance between community concerns and the need for new residential options, the real estate sector can adapt to rapidly changing demographics and preferences, ultimately leading to a healthier housing market.
The Economic Ripple Effects of Housing Affordability
The repercussions of the housing affordability crisis extend beyond individual homeowners and renters; they influence the broader economy as well. When housing is unaffordable, economic mobility is compromised, limiting opportunities for employment, education, and overall community development. Glaringly, a generation of potential homeowners is being forced to delay one of life’s major financial milestones, which holds significant implications for economic growth.
Additionally, high housing costs can lead to increased demand for government assistance programs, straining public resources. As families struggle to make ends meet, the strain on local economies becomes evident, often leading to increased taxes or reduced funding for essential services. Therefore, addressing the housing crisis is not only a matter of providing roofs over people’s heads but also an imperative for fostering economic stability.
Empowering Builders to Innovate: Overcoming Regulatory Barriers
To combat the housing crisis effectively, it is imperative to empower builders to innovate and embrace contemporary construction methodologies. This calls for a robust examination of existing regulations and a collaborative approach between governments, builders, and communities. By rethinking zoning laws and streamlining the permitting process, municipalities can turbocharge housing production while still adhering to community standards.
Ultimately, reducing barriers for builders fosters an environment ripe for innovation, encouraging the development of new housing types and models that meet a diverse array of needs. Without proactive measures to uplift the building sector, the stagnation in productivity will persist, perpetuating the cycle of high costs and unaffordable housing solutions.
Future Housing Policies: Addressing Affordability and Development
As discussions surrounding housing affordability evolve, it is essential for policymakers to implement future housing policies that prioritize both accessibility and development. Comprehensive strategies are required to address the nuances of the housing market while recognizing the need for sustainable growth. This could include financial incentives for builders who prioritize low-income housing and affordability in their projects.
Furthermore, bridging the gap between developers and local communities is crucial in creating harmonious environments where new homes can be integrated into existing neighborhoods without resistance. By fostering dialogues that highlight mutual benefits, policymakers can encourage the development of affordable housing in tandem with community interests.
Comparative Housing Models: Learning from International Examples
While the U.S. grapples with its housing crisis, examining comparative housing models from around the world can yield valuable insights. Numerous countries have successfully implemented innovative approaches to housing that prioritize affordability and accessibility. By looking at successful international case studies, U.S. policymakers can identify effective strategies to implement and adapt within their own communities.
From Denmark’s strong social housing commitments to Singapore’s public housing programs, international successes highlight the potential of collaborative approaches between government, private sector, and community stakeholders. Learning from these models can enable the U.S. to reshape its housing policies and practices to better serve diverse populations and combat the ongoing crisis.
Technological Innovations in Construction: Enhancing Housing Affordability
Technological advancements in construction methods are playing an increasingly vital role in addressing the housing affordability crisis. Innovative practices such as modular and prefabricated housing hold great promise for improving productivity and efficiency within the sector. By embracing new technologies that streamline the construction process, builders can deliver homes at a lower cost and in reduced timelines.
Additionally, advancements in smart home technologies can ensure that new constructions are not only affordable but also energy-efficient, further lowering overall living costs for future homeowners. The integration of technology into residential building processes offers a dual opportunity: reducing costs while enhancing the quality and sustainability of housing.
The Role of Community Engagement in Housing Development
Community engagement stands at the heart of effective housing development, particularly in the context of navigating NIMBY sentiments. By fostering open lines of communication between builders and the community, there is potential for collaborative solutions that address concerns while also promoting necessary housing developments. This interactive process can educate residents on the benefits of new projects and highlight the necessity of affordable housing.
Involve community members in the planning process establishes trust and encourages buy-in as developers address local needs. As a result, housing projects that incorporate the input and preferences of potential residents not only gain support but also foster a sense of ownership and pride among community members.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is contributing to the housing crisis in the USA?
The housing crisis in the USA is largely driven by the lack of housing affordability, which has escalated due to rising home prices and increasing construction costs. A significant factor in this crisis is the restrictive land use policies often referred to as ‘NIMBY’ (Not In My Backyard), which limit the scale and productivity of housing construction. These regulations stifle innovation among builders, leading to fewer large-scale housing developments that could alleviate housing shortages.
How does NIMBYism affect housing affordability in the USA?
NIMBYism negatively impacts housing affordability in the USA by enforcing stringent land-use regulations that limit new housing developments. When communities resist the construction of new homes, it reduces housing supply, driving up prices and making homeownership unattainable for many Americans. This creates a situation where construction productivity declines, further exacerbating the housing crisis.
What role does construction productivity play in the housing crisis?
Construction productivity plays a critical role in the housing crisis by directly influencing the cost of building homes. As productivity has stagnated since the 1970s, fewer homes are being built per worker, leading to higher prices. The decline in construction productivity is often linked to restrictive land-use regulations and a shift to smaller, less efficient building projects, which limits the benefits of economies of scale.
Why is housing affordability declining in the U.S.?
Housing affordability in the U.S. is declining due to a combination of rising construction costs, stagnant wages, and inadequate housing supply. Over the years, effective land-use policies and NIMBYism have restricted large-scale construction, contributing to decreased productivity in housing. As a consequence, home prices have surged, making it increasingly difficult for many Americans to afford homes.
What trends are we seeing in the U.S. housing market?
Current trends in the U.S. housing market include skyrocketing home prices and a noticeable decrease in home construction productivity. As large builders retreat from developing extensive projects due to NIMBY-style regulations, there is an increased reliance on smaller contractors, which limits growth and innovation in housing. Furthermore, demographic shifts and rising demand continue to strain the housing market, contributing to the ongoing affordability crisis.
How do real estate trends correlate with the housing crisis in the USA?
Real estate trends indicate a pervasive housing crisis fueled by rising prices, limited inventory, and increased demand. Factors such as labor shortages and escalating material costs, compounded by strict land-use regulations, have resulted in slower construction rates and decreased housing supply, all of which are critical elements of the current housing crisis in the USA.
What solutions are there to improve housing affordability in the USA?
To improve housing affordability in the USA, potential solutions include reforming restrictive land-use policies that bolster NIMBYism, incentivizing large-scale housing projects, increasing the use of innovative construction techniques, and improving infrastructure support for new developments. Addressing these factors could enhance construction productivity and help stabilize the housing market.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Housing Affordability Crisis | Homeownership is increasingly out of reach for many Americans, with the price of new single-family homes more than doubling since 1960. |
| Impact of NIMBY Policies | Restrictive land-use regulations stifle production by mandating smaller and bespoke housing projects. |
| Decline in Construction Productivity | Between 1970 and 2000, housing construction productivity decreased even as the overall economy grew. |
| Size of Homebuilding Companies | Current builders are significantly smaller than those of the past, reducing their efficiency and innovation capacity. |
| Historical Productivity Trends | From 1935 to 1970, housing construction productivity increased; since then, it has stagnated alongside rising regulations. |
| Economic Inequality in Housing Wealth | Wealth disparity is growing between age groups, with younger generations holding significantly less housing wealth than older generations. |
Summary
The housing crisis in the USA is significantly impacted by various factors, particularly the restrictive land-use policies that inhibit productivity and innovation in the construction sector. As housing costs continue to climb, it becomes clear that the rush of regulation—often stemming from NIMBY sentiments—has constructed barriers to effective housing production, leading not only to higher costs but also to a stark decline in the size and output capabilities of the homebuilding industry. As a result, the dream of homeownership slips further away from many Americans, deepening the economic divide and highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive housing policy reform.