Housing productivity is a critical factor in addressing the ongoing housing affordability crisis plaguing the U.S. housing market. Recent studies reveal that stringent land-use regulations and the hindering effects of NIMBYism have significantly stifled the productivity and innovation of builders, ultimately driving up housing costs for many Americans. As the demand for homes escalates, the inability to adopt construction innovations further complicates the issue. The burgeoning imbalance between supply and demand reinforces the need for a reevaluation of these regulations to enable a more productive housing sector. This is a pressing concern not only for potential homeowners but also for the overall economic wellbeing of the nation.
The concept of housing productivity encompasses the efficiency and output levels in residential construction. In recent discourse, terms like housing output and construction efficiency are often used interchangeably to discuss the struggles facing the housing sector today. Factors such as restrictive land use policies and community opposition to new developments, often referred to as NIMBYism, significantly impact the capacity for builders to innovate and meet increasing housing demands. Without addressing these challenges, the gap in housing availability will continue to widen, exacerbating the affordability crisis that has reached unprecedented levels in urban areas across the United States. Consequently, rethinking regulatory frameworks may be essential for revitalizing productivity and ensuring more accessible housing for all.
Understanding NIMBYism and Its Impact on Housing Development
NIMBYism, or ‘Not In My Back Yard’, refers to the opposition from local residents against new developments being constructed in their neighborhoods. This phenomenon has significantly influenced housing policy and development in the United States, contributing to a stagnation in building productivity. Community members often cite concerns such as increased traffic, potential noise pollution, and changes in neighborhood aesthetics as reasons for their resistance. However, these concerns can overshadow the pressing issue of housing shortage, exacerbating the housing affordability crisis across various demographics.
As land-use regulations tighten due to NIMBY sentiments, builders are often left with less room to maneuver in terms of project scale and innovation. Restrictions on project size and design limit economies of scale that previously allowed construction firms to operate efficiently. Instead of focusing on mass-produced homes that could provide affordable housing options, builders are forced to navigate complex local regulations that lead to bespoke developments. This not only affects housing costs but also stifles innovation within the construction sector, leading to a decline in productivity.
The Role of Land-Use Regulations in Housing Affordability
Land-use regulations have become more stringent over the years, promoting a decrease in housing construction productivity. These regulations often stem from NIMBY attitudes that prioritize the interests of existing homeowners over those seeking affordable housing options. Such policies can include zoning laws that limit the type and density of housing that can be built, ultimately leading to a decrease in the total number of units available for purchase or rent. As a result, housing becomes less affordable, particularly for younger generations and those with lower incomes who are struggling to enter the homeownership market.
Research indicates that as these regulations have proliferated since the 1970s, the size and scope of housing developments have notably diminished. Large-scale projects, once the norm in U.S. housing development, are becoming increasingly rare. The shift toward smaller, more manageable projects appeals to local residents but fails to address the broader challenge of a growing housing supply shortage. This duality highlights the complexity in balancing community preferences while fostering an environment conducive to increased housing production, which is crucial for tackling the housing affordability crisis.
Exploring Construction Innovation and Its Decline
The decline in innovation within the construction industry can be linked directly to the constraints imposed by land-use regulations. Historically, the construction sector thrived on innovations in materials, techniques, and project management that drove down costs and increased productivity. However, with the rise of NIMBYism and its accompanying land-use policies, there has been a significant drop in the patenting of new construction technologies. Builders are now reluctant to invest in innovative practices as the uncertainty surrounding project approvals and local community pushbacks diminishes potential returns on investment.
Without the incentive to innovate, builders are left relying on outdated practices, resulting in higher costs for consumers. The stagnation of construction innovation is particularly evident when compared to other sectors, such as manufacturing, which has continued to evolve and adapt to modern demands. For the U.S. housing market to recover and grow, a revival of innovation is necessary—a process that hinges on reducing excessive land-use regulations and embracing construction methods that can meet the needs of today’s inhabitants.
The Housing Affordability Crisis: A Growing Concern
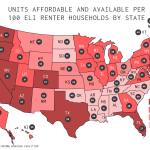
The housing affordability crisis is increasingly affecting many American families, with rising costs making homeownership unattainable. The price of new single-family homes has drastically increased, doubling since 1960, primarily due to several intersecting factors, including the escalating costs of labor and materials. When combined with stagnant wages and increasing land-use regulations, the barrier to affordable housing grows even more formidable. This issue impacts younger generations especially hard, who are unable to compete with older generations for available housing stock, resulting in significant economic inequality.
Furthermore, the scarcity of affordable housing options often forces families to move to areas with lower costs but potentially limited job opportunities, which detracts from overall economic productivity. As the U.S. formalizes urban sprawl and suburban development, addressing the shrinking availability of affordable housing units must become a priority. Solutions could involve reforming land-use regulations to allow more varied housing types and increasing the scale of housing developments, thus improving access to affordable options for all.
The Disconnection: Economy and Housing Development
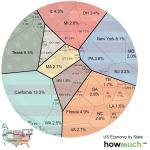
Despite strong growth in the general U.S. economy, the housing market tells a different story. The productivity of the construction sector has lagged significantly, as the introduction of restrictive land-use regulations has stunted growth compared to other industries. This disconnection creates a paradox where economic prosperity is not reflected in the housing market, showcasing how intertwined these systems are. A robust economy should ideally support increased housing production, yet the current regulatory environment inhibits builders from responding effectively to demand.
As the economy continues to thrive, the housing sector remains a critical area that needs reform. Addressing the discrepancies between economic productivity and housing development is necessary for a balanced approach to economic growth. Engaging with policymakers, builders, and community members will be essential in crafting land-use regulations that facilitate rather than hinder housing development, ensuring that all citizens have access to affordable housing in an otherwise prosperous economy.
Examining the Past: Historical Perspectives on Housing Construction
Studying historical data reveals that construction productivity has dramatically shifted over the decades, particularly post-1970. Early in the 20th century, housing construction saw rapid growth and innovation driven by a less restrictive regulatory environment. As big builders capitalized on economies of scale, they effectively produced housing at a pace that matched growing demand. However, this trend began to reverse as NIMBY sentiments and land-use policies began to gain traction, leading to a decline in the number of homes constructed and an increase in project costs.
This historical perspective underscores the importance of understanding how past practices can inform current housing challenges. As researchers analyze the correlation between large-scale building projects and productivity, it becomes clear that reinstating elements of this previous success could alleviate current issues in the housing market. Recalibrating land-use regulations might allow for a renaissance in construction practices that prioritize efficiency and affordability, crucial for bridging the gap in the U.S. housing market today.
Future Prospects: Solutions to the Housing Crisis
Looking ahead, addressing the housing affordability crisis will require innovative solutions and a willingness to re-examine existing land-use regulations. Policymakers and community leaders must recognize the necessity of increasing housing production to support the growing population and meet diverse housing needs. Strategies might include easing zoning restrictions, promoting higher density developments, and incentivizing larger-scale projects that leverage economies of scale essential for affordable construction.
Additionally, fostering collaboration among builders, local governments, and community stakeholders can facilitate a more community-oriented approach to housing development. By actively engaging with residents to understand their needs while explaining the importance of increased housing supply, there is potential for a shift in the attitudes that have historically stymied construction. Through balancing community interests with the urgent necessity for affordable housing, the U.S. can work towards a future where homeownership is within reach for all.
Collaborating for Change Without Compromising Community Values
Achieving a balance between community values and the need for increased housing supply is essential in tackling the housing crisis. Encouraging constructive dialogue among stakeholders will be pivotal in reshaping the conversation regarding new developments. Community engagement initiatives can help to alleviate fears associated with new housing projects, thus mitigating NIMBYism’s impact. When residents feel their voices are heard and that they have a role in shaping their neighborhoods, they may become open to innovative housing solutions that better serve the community as a whole.
Moreover, leveraging sustainable construction practices can bridge the gap between development and environmental stewardship. By incorporating green technologies and investment in smart growth strategies, builders can appeal to community concerns regarding environmental impact. This approach not only serves to justify new projects but also provides meaningful incentives for communities to embrace change. Through successful collaboration, it is possible to create thriving neighborhoods equipped with both affordable housing options and the community amenities necessary for a high quality of life.
The Importance of Policy Reform in the Housing Sector
To address the persistent housing affordability crisis, substantial policy reform is necessary. This may involve revisiting existing land-use policies that serve to limit housing production and exploring alternative methods of zoning that promote higher density development and mixed-use projects. Comprehensive policy modifications can pave the way for creative housing solutions that fulfill the diverse needs of residents while ensuring economic viability for builders. Such reforms can stimulate both public and private sector engagement in housing efforts.
Furthermore, understanding the economic context in which these policies operate is critical. By aligning housing policies with broader economic objectives, authorities can invigorate the market and eliminate obstacles to production. Policymakers must recognize that housing is not merely about bricks and mortar but is intricately connected to overall economic health. Developing an integrated approach that focuses on sustainable urban development, equitable housing access, and productive housing markets will create an environment where both builders and communities can successfully thrive together.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does NIMBYism impact housing productivity in the U.S.?
NIMBYism, or ‘Not In My Backyard’ attitudes, significantly impacts housing productivity by enforcing stringent land-use regulations that restrict the scale and type of housing developments. These regulations often lead to smaller construction projects, which limit builders’ ability to achieve economies of scale, thus decreasing overall productivity in the housing market.
What role do land-use regulations play in the housing affordability crisis?
Land-use regulations contribute to the housing affordability crisis by hindering the mass production of homes, which keeps costs high. These regulations restrict the size and density of developments, making it difficult for builders to create affordable housing solutions, exacerbating the gap between housing prices and income levels.
Can construction innovation help improve housing productivity?
Yes, construction innovation can play a crucial role in improving housing productivity. By adopting new technologies, building techniques, and materials, the construction industry can reduce costs and increase efficiency, which can help to lower housing prices and address the affordability crisis.
What is the current state of the U.S. housing market regarding productivity?
The U.S. housing market is experiencing stagnation in productivity, largely due to the impact of land-use regulations and a decline in large-scale construction projects. This stagnation contributes to rising housing costs and an ongoing affordability crisis, as smaller builders, hindered by regulatory environments, struggle to innovate or scale.
How do economic factors correlate with housing productivity and construction innovation?
Economic factors such as labor and material costs, interest rates, and local regulatory environments directly correlate with housing productivity and construction innovation. A favorable economic climate that encourages innovation can lead to increased housing productivity, but high costs and restrictive regulations can suppress it.
What lessons can be learned from the decline of construction productivity since the 1970s?
The decline of construction productivity since the 1970s highlights the detrimental effects of NIMBYism and stringent land-use regulations, emphasizing the need for policy reforms that support larger-scale housing developments and encourage innovation in the construction industry to combat the housing affordability crisis.
How does the size of construction firms affect housing productivity?
Larger construction firms (with 500 or more employees) generate significantly higher housing productivity, producing four times as many units per employee compared to smaller firms. This disparity is largely because larger firms can leverage economies of scale, which are stifled by land-use regulations and NIMBY attitudes in many regions.
| Key Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| U.S. Housing Crisis | The housing affordability crisis in the U.S. stems from rising costs and stagnation in housing productivity. |
| Impact of Land-Use Policies | NIMBY policies stifle large-scale housing developments, thus inhibiting mass production and raising housing costs. |
| Construction Productivity Decline | Productivity in housing construction has decreased dramatically since the 1970s, impacting housing supply. |
| Economies of Scale | Larger construction firms build significantly more units than smaller ones, but the trend has shifted to smaller projects due to regulations. |
| Innovation Decline | The construction industry has lagged in patents and innovation since the 1970s compared to other sectors, influencing productivity. |
| Intergenerational Wealth Transfer | Younger generations possess significantly less housing wealth than older generations, raising concerns about economic stability. |
Summary
Housing productivity has become a critical issue affecting affordability and accessibility in the U.S. market. The combination of restrictive land-use regulations and a significant decline in construction innovation has resulted in a housing crisis where ownership becomes increasingly unattainable for many Americans. Addressing these challenges is essential for improving housing productivity and ensuring a stable housing market for future generations.